- Human migration – movement of people from one place to another with the intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily at new location.
- Types of human migration:
a. Internal migration (or domestic migration) is human migration within a country.
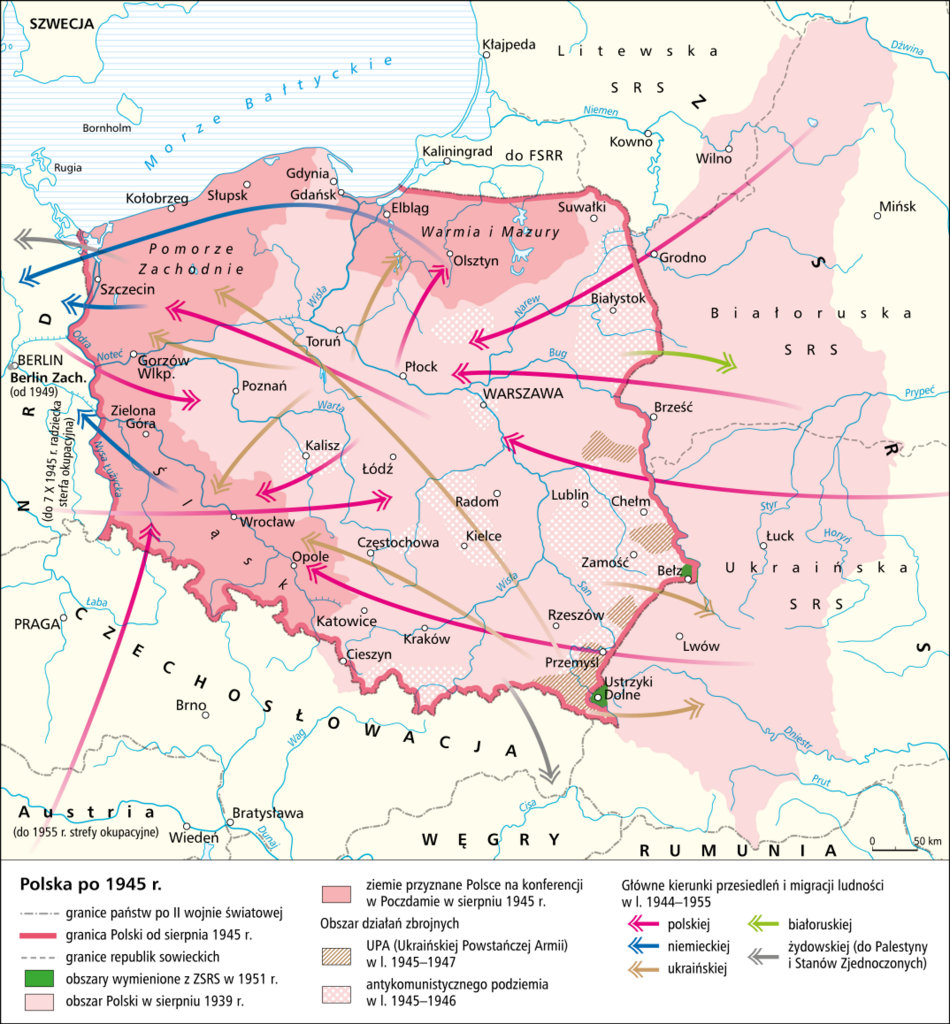
After the World War II under the National Repatriation Office (Państwowy Urząd Repatriacyjny), millions of Poles were forced to leave their homes in the eastern Kresy region and settle in the western former German territories.
b. Emigration – the act of leaving one’s country to settle permanently in another (moving abroad).
c. Immigration – the action of coming to live permanently in a foreign country.
d. A refugee (uchodźca) – a displaced person (wysiedleniec) who has been forced to cross national boundaries and who cannot return home safety.
* asylum seeker -osoba ubiegająca się o azyl
An asylum seeker is an immigrant who has been forcibly displaced and might have fled their home country because of war or other factors harming them or their family. He can applie for asylum.
Refugee is someone who is persecuted (it can be race, religion, nationality, membership in a particular social group, or political opinion).
The terms asylum seeker and refugee are often confused.
If asylum seeker’s case is accepted, they become considered a refugee.
Gdzie ludzie na świecie najczęściej migrują? Do jakich państw? (s. 138)
Why do people migrate?
2. The reasons for migrations:
a. economic migration – moving to find work or follow a particular career path
b. social migration – moving somewhere for a better quality of life or to be closer to famili or friends
c. political migration – moving to escape political persecution or war
d. enviromental causes of migration include natural disasters such as flooding
PUSH AND PULL FACTORS
Push factors are the reasons why people leave an area. For example” lack of services, lack of safety, high crime, flooding, poverty, war, crop failure (nieurodzaj), drought (susza), human rights violations.
Pull factors are the reasons why people move to a particular area. For example: higher employment, more wealth (zamożność), better services, good climate, safer or less crime, political stability, more fertile countries (żyźniejsze kraje), lover risk fram natural hazards (zagrożenia)
3. Waves of migration in Europe after Word War II.
– War caused that people had been arrived to Great Britain, Germany or France. They was used as a cheaper labour force (siła robocza).
– A huge reason for migration was the fall of Communism. People had been leaved their countries for economic reasons.
-In 2004 Poland was admitted to UE. EU citizens are free to move and work within the union.
– In 2015 – migration crisis. People from Afghanistan, Iraq and Syria. They tried to come to Europe ( through the territory of Italy or Greece).

4. Migration policies
a. Situation of imigrants depends on their legal status:
-if they are legally resident they have a permission to stay (pozwolenie), they can work, they have social benefits and they can apply for citizenship (ubieganie się o obywatelstwo).
-if they have a refugee status they are protected by international law.
-if they are illegaly resident they can be deported to their own country.
b. most countries are trying to help immigrants (but they have problems with hiring a job, language, different culture, lower qualiffications)
5. Immigrants in Poland
– from the countries of the former Soviet Union (z krajów byłego ZSRR) – mostly Ukrainians.
– Immigrants from Asia (China and Vietnam).
– African immigrants, who are studying in our country.
– Western immigrants (from USA and Western Europe).
- Kryzys migracyjny – i co dalej? ( str. 142)
- Zadania str. 143.
