The political system of the Republic of Poland is established by the Constitution of Poland (1997). Polish Constitution guarantees the freedom of individuals.
According to the Constitution Poland:
-is unitary semi-presidental representative democratic republic;
-is the state accomplishes the rules of independence, democracy, legal and civil rights of the citiziens along with pluralism and legalism.
*political pluralism – the existence of two or more political parties representing different programs and orientations
*legalism = rule of law (praworządność) – the legal principle (zasada, reguła ~ potwierdzona prawnie) that law should govern a nation, with everyone equal before the law (równi wobec prawa).
-carry out (=enforce – wprowadzać w życie, realizować) the separation of powers principle:
*Montesquieu’s separation of powers system = „tripartite system” – Montesquieu was a French political philosopher of the Enlightenment period, whose articulation of the theory of separation of powers is implemented in many constitutions in the world. He described three forms of distribution of political power.
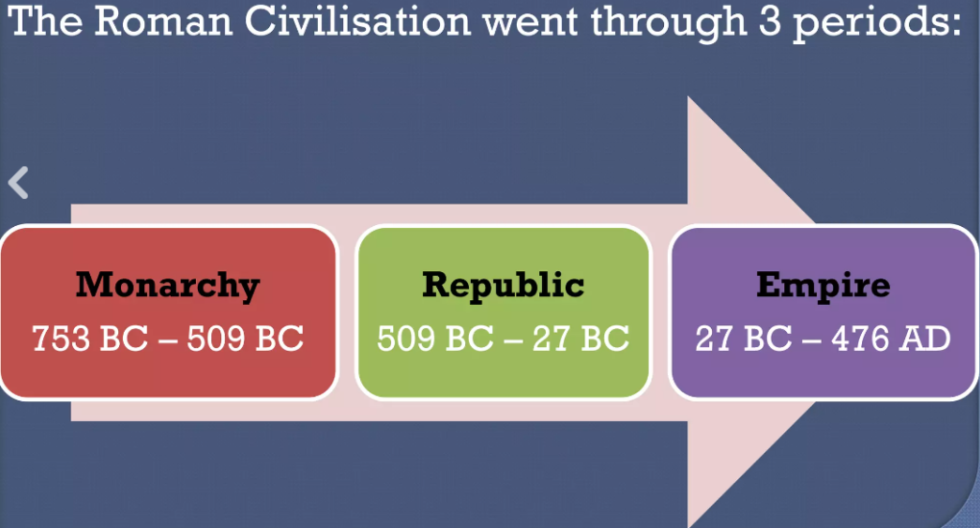
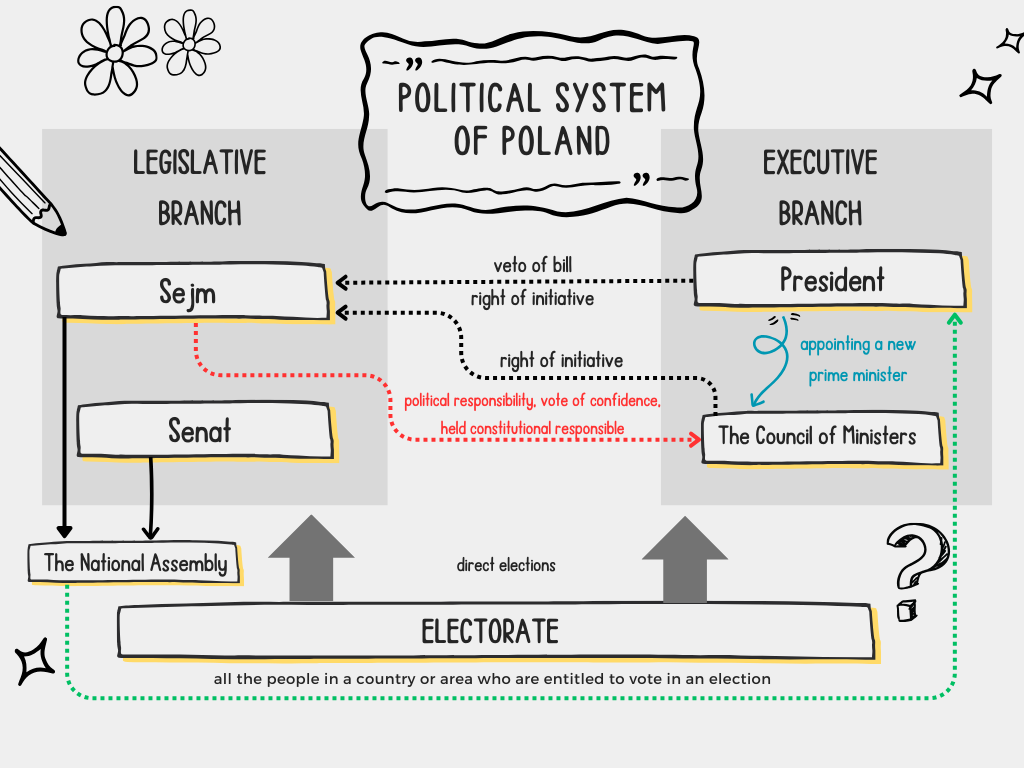
1. Legislative branch –> a legistrature –> legislative power – two chambers of Parliamnet (Sejm and Senate).
2. Executive branch –> an executive –> the President and the Government (the Council of Ministers led by the prime minister).
3. Judical branch –> a judiciary (the courts of law and the Constitutional Tribunal – can annul laws that violate the freedoms guaranteed in the constitution ).
LEGISLATIVE BRANCH
Sejm:
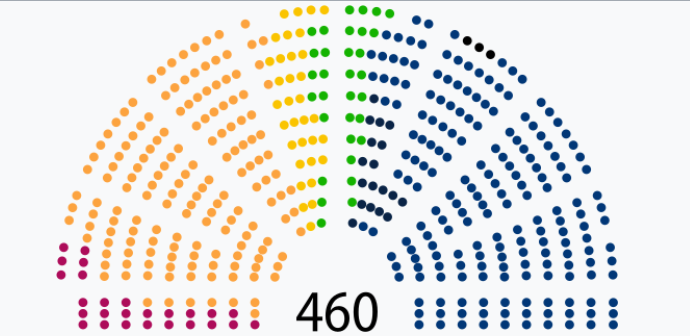
-the lower chamber
-460 members elected for a four-year term
Senate:
-the upper chamber
-100 members elected for a four-year term
The National Assembly
-is formed, when members of the Sejm and Senate sitting in joint session
-on three occasions:
*taking the oath (ślubowanie) of office by a new president
*bringing an indictment against the president of the republic to the Tribunal of State
*declaration of a President’s permanent incapacity to exercise their duties due to the state of their health
Main office-holders
Marshal of the Senate -Małgorzata Kidawa-Błońska (Civic Platform)
Marshal of the Sejm – Szymon Hołownia (Poland 2050)




EXECUTIVE BRANCH
President
-the head of state
-the supreme commander of the Armed Forces
-has the power to veto legislation passed by parliament
-can dissolve the parliament under certain conditions
-presidential elections occur every five years
-representative of the state in foreign affairs
The Council of Ministers
-the prime minister proposes, the president appoints, and the Sejm approves the Council of Ministers
-is responsible to the prime minister and the Sejm
Main office holders
President – Andrzej Duda – Law and Justice
Prime Minister – Donald Tusk – Civic Platform
JUDICAL BRANCH
common courts (sądy powszechne)
tribunals (trybunały)
administrative courts (sądy administracyjne)
military courts (sądy wojskowe)
appeal courts (sąd apelacyjny)
district courts (sądy okręgowe)
The Constitutional Tribunal (Trybunał Konstytucyjny)
The State Tribunal (Trybunał Stanu)
The National Council of the Judiciary (Krajowa Rada Sądownictwa)
The National Court Register (Krajowy Rejestr Sądowy)
Useful vocabulary:
Sejm Plenary Hall
Poland is divided in 16 provinces or Voivodeships
Electoral district – okręg wyborczy
Bicameralism – dwuizbowość