Civilization – human society with its well developed social organizations, or the culture and way of life of a society or country at a particular period in time.
Culture – the way of life, especially the general customs and beliefs, of a particular group of people at a particular time.
A civilization has often been understood as a larger and „more advanced” culture. Civilisation is a broader concept (szersze pojęcie) than the culture.
State – is a centralized political organization that imposes and enforces rules over a population within a territory.
Types of writting/scripts:
Cuneiform (clay tablets)

Egyptian hieroglyphs (Epigraphy )




MESOPOTAMIA is called „The land between rivers” – Euphrates and Tigris. Sometimes also called fertile crescent due to the rich soil (gleba), silt (muł), found there.
It included parts of what are now Iraq, Iran, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, and Israel.
- Natural conditions ( why there? )
- The state organization and political system:
a. Sumer,
b. Akkadian state,(Sargon z Akadu),
c. Babylonia,(Hammurabi, Nabuchodonozor), zasada talionu obowiązywała tylko wolnych obywateli, jeżeli poszkodowanym był niewolnik lub tzw. człowiek królewski płacono grzywnę
d. Assyria (Sargon II, Aszurbanipal, Tiglatpilesar)
e. despotism (monarchia despotyczna)
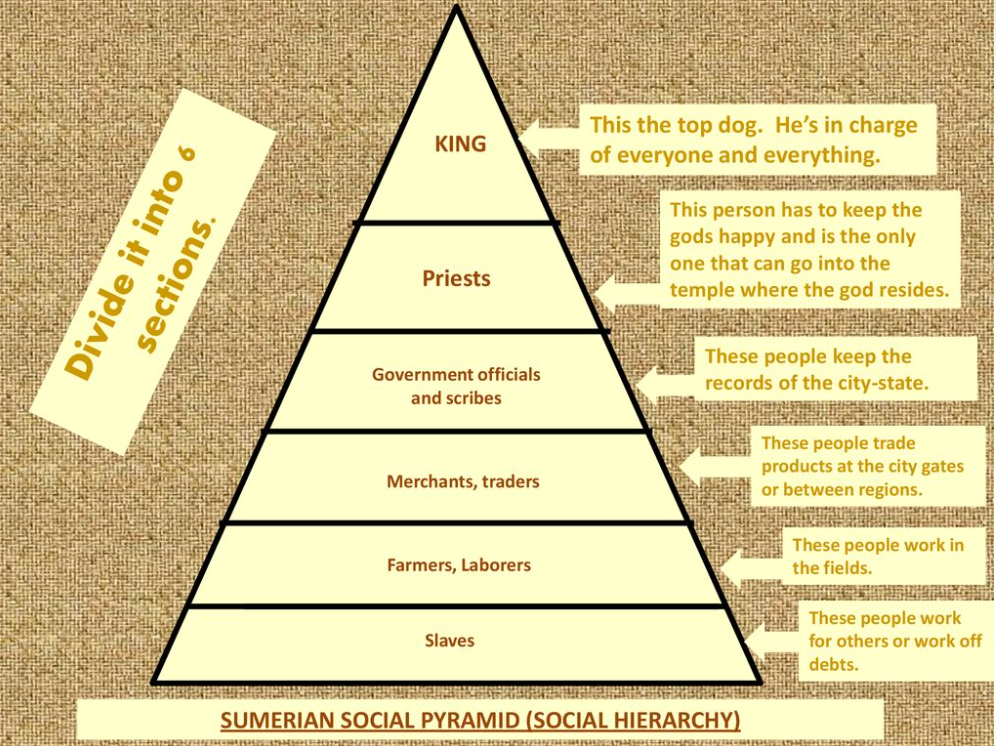
f. society – społeczeństwo (warstwa panująca i kapłani, ludzie wolni, ludzie zależni od świątyni – ludzie królewscy, niewolnicy)
Religia i wierzenia
– Polytheism (politeizm)-is the belief in multiple deities or goods
Osiągnięcia
Źródło: Materiał pobrano i udostępniono ze strony https://slideplayer.pl/slide/13089815/

Zasada talionu – lex talion- law of exact retaliation – „An eye for an eye” principle – kara jest identyczna jak skutek przestępstwa (kara odzwierciedlająca).

STRONA O CYWILIZACJI SUMERÓW – proszę poczytać o bogach sumeryjskich: https://www.starozytnysumer.pl/podstrony/bogowie.html

